Console Credentials
This step is optional, as nearly all of the workshop content is CLI-driven. But, if you’d like full access to your workshop cluster in the EKS console this step is recommended.
The EKS console allows you to see not only the configuration aspects of your cluster, but also to view Kubernetes cluster objects such as Deployments, Pods, and Nodes. For this type of access, the console IAM User or Role needs to be granted permission within the cluster.
By default, the credentials used to create the cluster are automatically granted these permissions. Following along in the workshop, you’ve created a cluster using temporary IAM credentials from within Cloud9. This means that you’ll need to add your AWS Console credentials to the cluster
Import your EKS Console credentials to your new cluster:
IAM Users and Roles are bound to an EKS Kubernetes cluster via a ConfigMap named aws-auth. We can use eksctl to do this with one command.
You’ll need to determine the correct credential to add for your AWS Console access. If you know this already, you can skip ahead to the eksctl create iamidentitymapping step below.
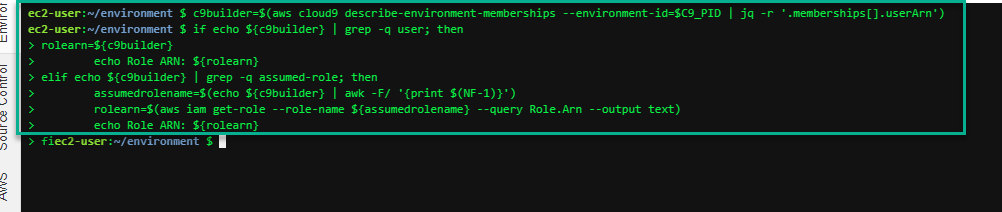
If you’ve built your cluster from Cloud9 as part of this tutorial, invoke the following within your environment to determine your IAM Role or User ARN.
c9builder=$(aws cloud9 describe-environment-memberships --environment-id=$C9_PID | jq -r '.memberships[].userArn')
if echo ${c9builder} | grep -q user; then
rolearn=${c9builder}
echo Role ARN: ${rolearn}
elif echo ${c9builder} | grep -q assumed-role; then
assumedrolename=$(echo ${c9builder} | awk -F/ '{print $(NF-1)}')
rolearn=$(aws iam get-role --role-name ${assumedrolename} --query Role.Arn --output text)
echo Role ARN: ${rolearn}
fi
With your ARN in hand, you can issue the command to create the identity mapping within the cluster.
eksctl create iamidentitymapping --cluster eksworkshop-eksctl --arn ${rolearn} --group system:masters --username admin
Note that permissions can be restricted and granular but as this is a workshop cluster, you’re adding your console credentials as administrator.
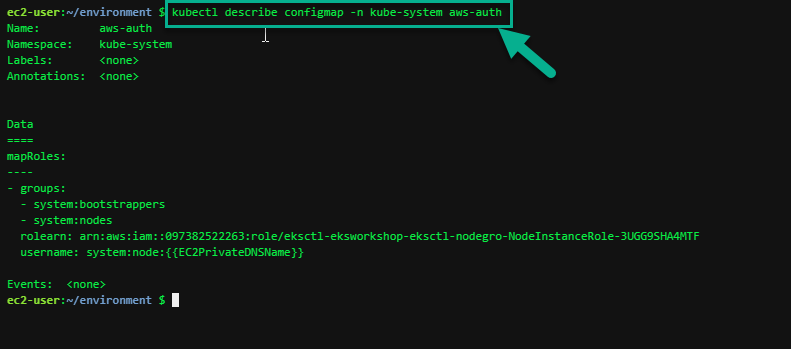
Now you can verify your entry in the AWS auth map within the console.
kubectl describe configmap -n kube-system aws-auth
Now you’re all set to move on. For more information, check out the EKS documentation on this topic.